how do contact lenses work physics
Revisit the physics of how lenses work and how refraction spherical aberration and chromatic aberration come about. How Contact Lenses Work Contact lenses are designed to capture and reflect light in a manner that corrects the way your eyes process light.
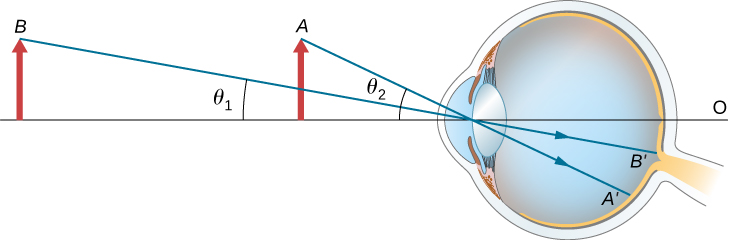
The Simple Magnifier University Physics Volume 3
Since the lenses stick to the tear fluid on your eye surface they move naturally with you.

. This moves the eyes focus point forward onto the retina. This moves the eyes focus point backward onto the retina where it belongs How Do Contact Lenses Work. You can read a full explanation of why this happens in our article on light That means the rays seem to come from a point thats closer or further away from where they actually originateand thats what makes objects seen through a lens seem either.
Contact lenses and glasses correct farsightedness by converging light rays which increases the eyes focusing power. The lens is clear but when exposed to. Contacts also correct some corneal astigmatism caused by surface irregularities.
Contact lenses help form the image on the retina of the eye by either converging or diverging the rays of light entering the eye. But what is the science behind artificial perfect vision. In other words contact lenses work by fine-tuning the light into your eyes.
It bends light rays as they pass through it so they change direction. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. Contact lenses work in much the same way as prescription glasses.
Again as for concave mirrors the answer lies in the relative distance between the focal distance and the object. In equation form this is P 1 f P 1 f where f is the focal length of the lens which must be given in meters and not cm or mm. Modern contacts are much more than small eye glass lenses that fit onto your eyes.
The power of a lens P has the unit diopters D provided that the focal length is given in meters. They do however function much like regular eye glassesrefracting and focusing light so that objects appear clearly. Scleral lenses are large contact lenses that cover the complete sclera - the white outer coating -.
Lens powers that correct nearsightedness start with a minus sign and lens powers that correct farsightedness start with a plus sign. The tear layer between the smooth contact and the cornea fills in the irregularities. The curve of the image must be matched to the curvature of the retina.
How Do Multifocal Contacts Work Multifocal Lenses Pros Cons. If you have a refractive error you may have myopia nearsightedness astigmatism hyperopia farsightedness or presbyopia age-related farsightedness. How do lenses work.
The converging lens lowers the focal length of the light and this proportionally reduces the distance of. Contact lenses are plastic devices that rest on top of your cornea and correct a refractive error. The lens lies between the retina and the pupil.
The inverse of focal length is the refracting power usually just called power of the lens and the inverse of the object and image distances are called vergencesUsing these new terms the lens equation can be stated more compactly in words and symbols. We can explore why some lenses make images bigger why the film in a movie projector has to be upside down to get a right side up projected image and how contact lenses work all with ray diagrams. They are used in telescopes to help view items that are far away and are used in microscopes to help view very small items.
Contact lenses and glasses correct farsightedness by converging light rays which increases the eyes focusing power. Contact lens and eyeglass lens powers are expressed in diopters D. When a light wave moves from one medium like air to.
The contact lens that is convex or converging in nature is used to correct this condition. For myopia Contact lenses and eyeglasses correct nearsightedness by diverging light rays which reduces the eyes focusing power. This moves the eyes focus point forward onto the retina.
Its similar to a magnifying glass. Its similar to a magnifying glass focusing a beam of sunlight on one specific spot. The cornea is a transparent covering of the lens as shown in the diagram above.
Lots of contact lens patients start to lose interest in contacts when Presbyopia a loss of ability to focus the eyes on near objects starts to take away their up-close vision. The light must focus at the surface of the retina. Contact lenses are used for nearsighted and farsighted issues in different ways.
A lens is a curved piece of glass or plastic designed to refract light in a specific way. Once the contact is in it redirects light into a single focal point on the retina. In a ray diagram a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to.
Lenses are used in glasses and contacts to help correct vision. If I do I die It is often more convenient to work with this equation if we give special names to the inverse quantities. Because contacts cover a significant portion of the cornea they provide superior peripheral vision compared with eyeglasses.
Contact lenses work in the same way as glasses by adding or subtracting wavefront curvature. These three things are accomplished by the eyes lens and cornea. That is 1D 1 m or 1m1 1 D 1 m or 1 m 1.
Heather Brown talks with a Twin Cities op. This is but one advantage contacts have over glasses. Lens powers that correct nearsightedness start with a minus sign and lens powers that correct farsightedness start with a plus sign.
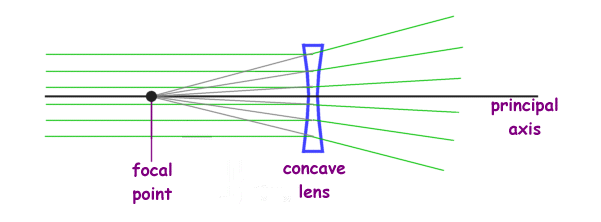
Many people have more than one refractive error. Leaves tip travels parallel to principle axis refracts and travels through to the focus. A lens works by refraction.
How do photochromatic lenses work. Leaves tip travels through focus on same side travels through lens and exits lens parallel to principle axis on opposite side. This basically adjusts where the focal point of light entering the eye is glasses and contact lenses are designed to adjust it so that the focal point of the light lies on the retina.
It fine-tunes and focuses the light that enters your eyes. Photochromatic lenses are commonly called transition lenses. There are now excellent MULTIFOCAL CONTACTS available that allow patients over age 40 to wear contacts.
Contact lens and eyeglass lens powers are expressed in diopters D. Leaves tip passes straight through center of lens and exits without bending. Have more questions about lenses.
Earlier contact lenses were made of glass and were scleral lenses. Contacts change the direction of light coming into the eye so that it focuses on the retina on a single focal point. They come together at a point called the principal focus.
Three-quarters of us wear some sort of corrective lenses.

The Remarkable Technology Of Our Human Eyes Cannot Be Replicated At Least Not Yet Quartz
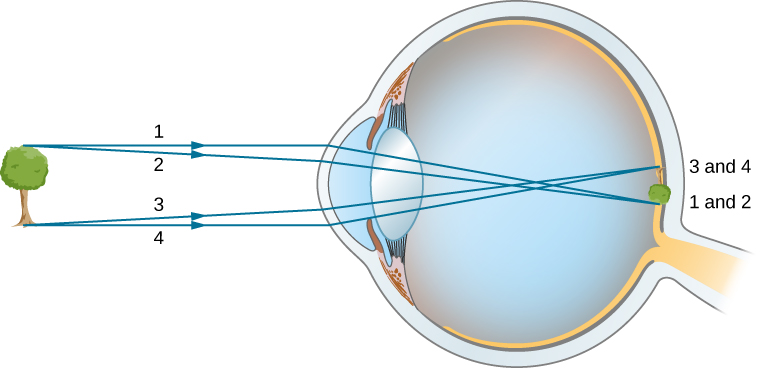
The Eye University Physics Volume 3

Lens Meaning Principles Manufacture Facts Britannica
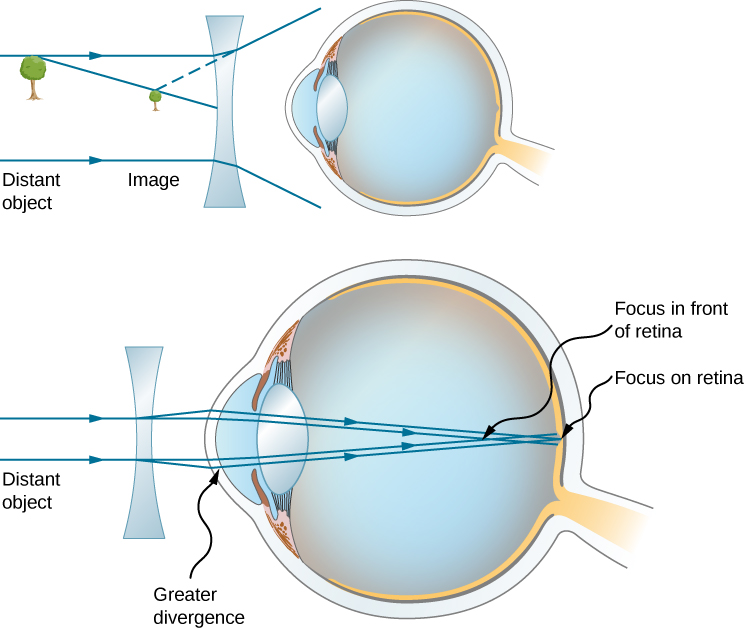
The Eye University Physics Volume 3
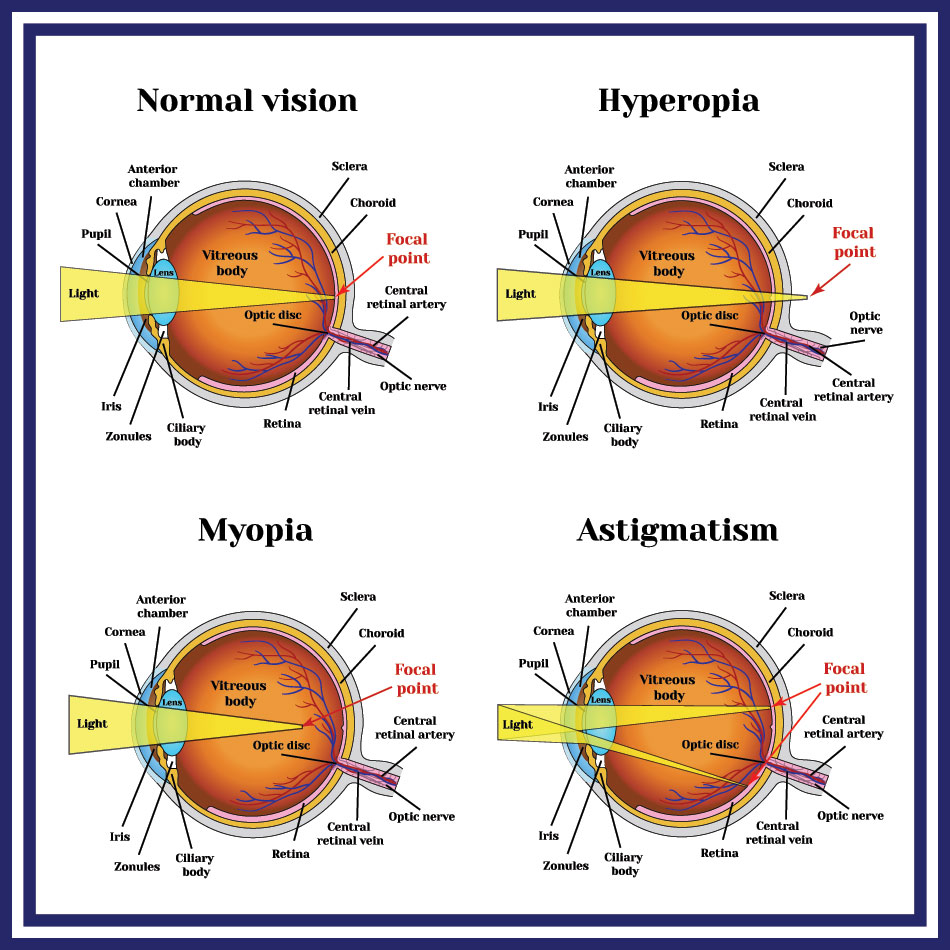
How Do Contact Lenses Work The Science Behind Them Lenspure
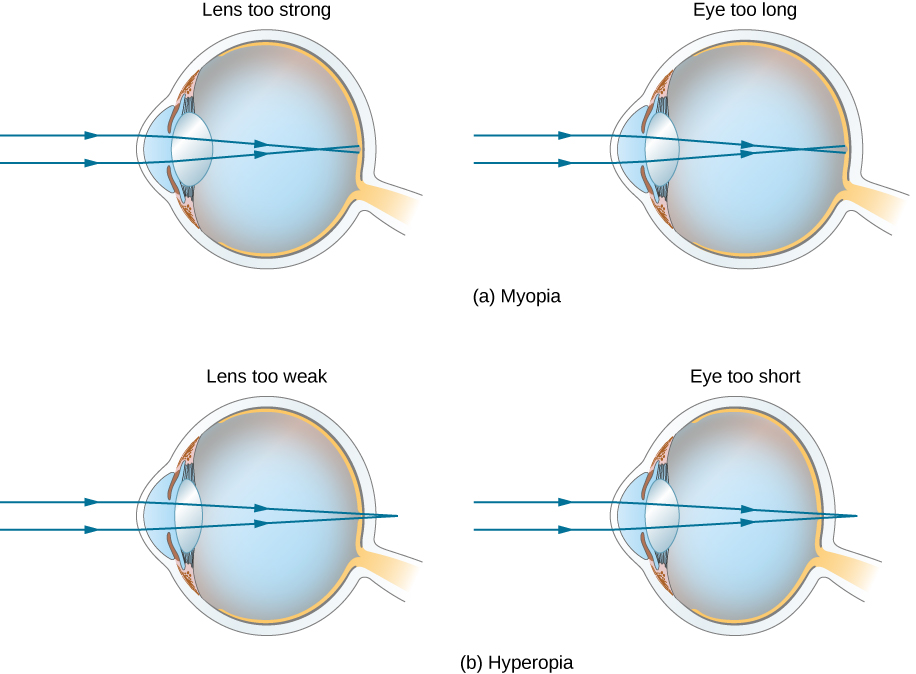
The Eye University Physics Volume 3
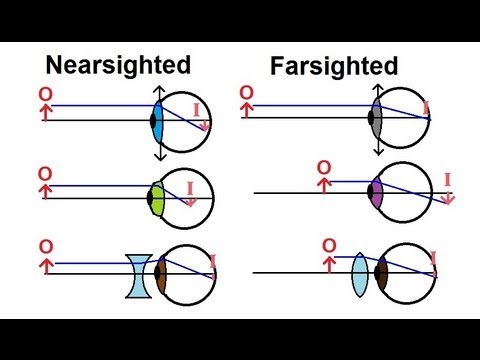
Physics Optics Vision Correction 1 Of 5 Introduction Youtube
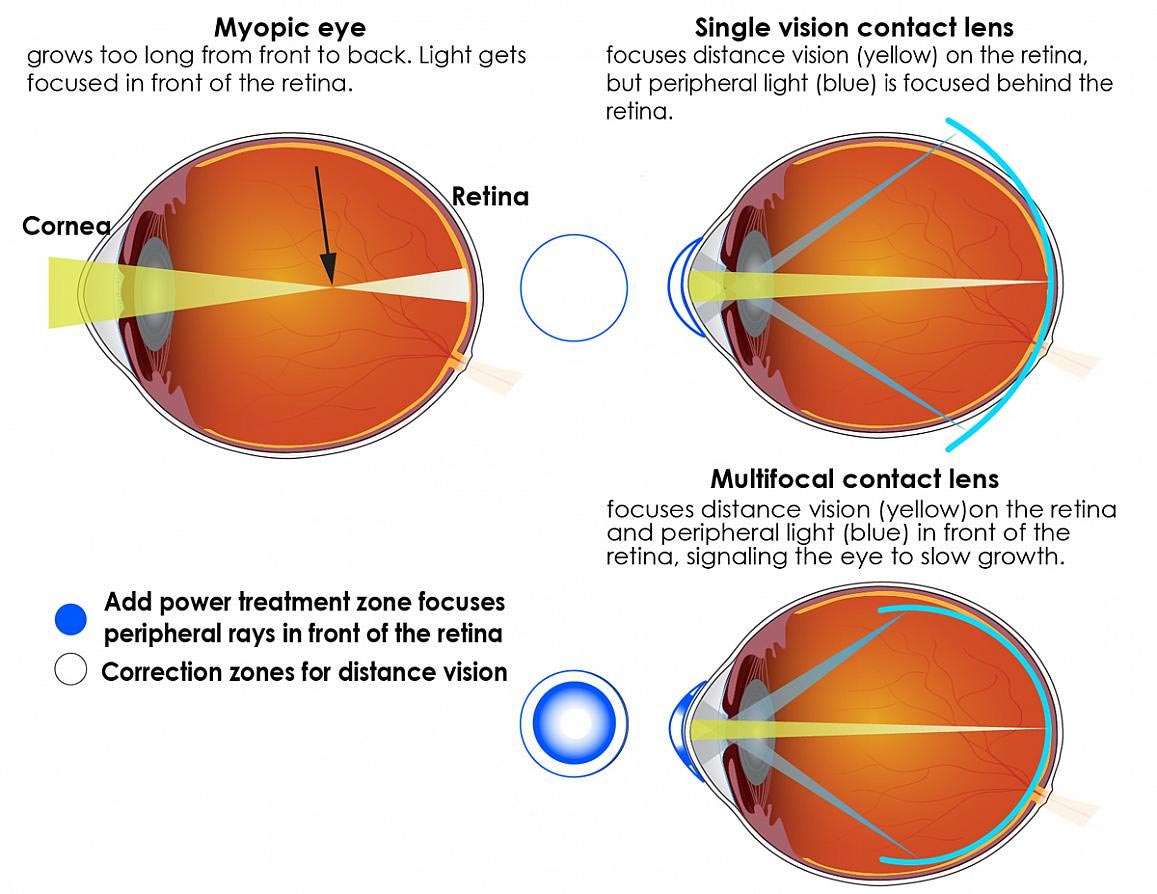
Multifocal Contact Lenses Slow Progression Of Nearsightedness In Children

The Science Of Eyeglasses Williams Eye Works

Physics Optics Vision Correction 1 Of 5 Introduction Youtube